
|
Olympus E-M1 Mark II Compared to the original of 2013 |

|
My other articles related to the |
|
My description and remarks on the original E-M1 are in separate posting; here I am describing the features changed or new in the current version. |
|
Table of Contents: | ||||
|
At the first glance, the new model looks, feels, operates and delivers very much like the original. Under the hood, however, almost no stones were left unturned, and a closer look shows changes in camera's behavior and (some of the) results. Let me quickly list the changes, in no particular order, but starting from the outside.
Now, the not-so-obvious changes inside (most will be discussed in detail later). I am comparing here the Mark II model to the original E-M1 with firmware updated to Version 4.3 — this is important, as Olympus was, in case of this camera, very generous in adding or changing features by firmware revisions.
The Body: Size, Make and Finish As similar as it may seem, this is a completely new body cast — a costly investment by Olympus. The new body is built of magnesium alloy and aluminum (I guess the British version uses aluminium instead). The body is splash-, dust- and freeze-proof, and so are some of the better μFT lenses. Anyway, a premium job. The Mk.II body is a tad bigger than the original one. Here is a comparison with other members of the E-MD line. (W×H only, as the depth does not really matter; weight includes battery and cards.)
The height numbers are a bit misleading. While the Mk.II is shown here as being 3 mm shorter than its older sibling, this is due to a significant reduction in the size of the viewfinder hump (removal of the proprietary accessory port I never liked); the height of the body proper, measured to the top deck, actually increased quite significantly, by about 5 mm (using the mode dial as reference point). Note the 14% increase in camera's weight, too. | ||
.t.jpg)
|
.t.jpg)
| |
|
The bodies of both EM-1 versions, shown in the same scale. (Images by Olympus) | ||
|
We can see that the controls are arranged in exactly the same fashion, but the top deck was completely re-sculpted. Note different placement of strap lugs: the right one sometimes used to cause some inconvenience; a small but appreciated improvement. A view from behind, can be also quite revealing, as it is often the case. | ||
.t.jpg)
|
.t.jpg)
| |
|
Both bodies, seen from behind, same scale (or close). | ||
|
Note slightly different button arrangement at bottom-right and the changed orientation of the Fn mode lever to the right of the finder. The thumb rest is now a bit more prominent, and the advantages of getting rid of the accessory port below the hot shoe seem quite obvious.
I tend to prefer, if not by much, the smaller weight and size of the older model, but this is a matter of personal preference. One thing I still dislike about the body are the rubber flaps, protecting the sockets on both sides of the body. They just don't feel right, and attaching a USB Type C plug (cable included with camera) requires more patience and dexterity than I would like it to. Worse, this design makes it simply impossible to tilt the monitor while the USB cable is plugged in, like in tethered shooting. Most annoying. The new monitor tilts and swivels (the old one would just tilt up and down). While this will please some people (most of all, reviewers), the solution has some disadvantages for those who use it mostly in landscape orientation: it is less compact, with the whole length of the monitor sticking out to the left of the camera (or down, if in portrait orientation). I use monitor for viewing mostly for two purposes: tabletop and ground-level nature photography (or something similar). In-place tilt is what I prefer in those situations. True, you are limited to the landscape orientation, but try to switch to portrait and use the swivel with the new camera: it becomes awkward, to say the least. OK, opinion-shaping reviews demand tilt-and-swivel, so this is what we all get, like it or not (four legs good, two legs bad). Besides, no respectable photographer will use a camera without a selfie capability: making stupid faces with Taj Mahal in the background becomes a must. People, don't you have cell phones to do that? At the first glance the electronic, eye-level viewfinder looks unchanged from the original (or from the E-M5 Mk.II upgrade). The same resolution of 2.36 million color dots (767 thousand RGB pixels), the same effective magnification of 0.74×, the same layout (with just a few minor information items added). This is, however, just on the surface. Olympus claims an improved refresh rate of 120 frames per second (up from some unspecified value in the original E-M1) and the reduction in latency (viewed image delay) from 23 to just 5 ms (here at least we have both values, even if some sources quote 29 and 6 ms). The increase in refresh rate should, I would think, reduce the jagged finder view when the camera is panning. I had no complaints here with the original E-M1, so I'm really hard pressed to see any improvement in Mark II. Really, a side-by-side comparison, with both cameras using the same lens — nothing. Well, maybe it takes a trained eye. Still, the numbers say the new finder must be better, even if I can't see it... This is the first OM-D camera with a 20MP image sensor. The 25% gain in pixel count means a 12% increase in (linear) resolution: from 4608×3456 to 5184×3888 pixels. While this is not a large increase (and pixel count is no longer a major determinant of image quality), camera makers keep adding megapixels, if mostly for marketing reasons. The good news is that the resolution of better μFT lenses is still high enough to use those extra pixels for image detail. The new sensor shares one unique feature with its 16MP sibling used in the original E-M1: some of its green photosites have been replaced with light receptors used for on-chip phase-detection AF. This allows for full AF functionality of all legacy Four Thirds lenses when used on the new camera. The improved performance of the finder is related to the overhaul of the Olympus image-processing engine, a part of camera's firmware. The firmware deals with more things than just image processing: autofocus and image stabilization being the obvious heavyweights — when active, they both work real-time. The TruePic engine progressed from Version VII to Version VIII. Looks like this time it is not just a matter of slapping a new number on an old horse; all signs show that (almost) no stones were left unturned, as we will see further down. To provide enough processing power, the designers equipped Mark II with two processors, each with four computing cores. That's eight threads; roughly: eight tasks running at one time, without holding some to push ahead with others. Image processing supposedly is 3.5 times faster than on TruePic VII. Some Olympus sources refer to one of these processors as CPU, ant the other — as graphics processors, without going into any details. All this is styled to look like technical information. but it really isn't. We are getting no clue how it compares to other cameras (Olympus or not), not to mention any benchmarks. Still, I do believe the new engine has not only new or improved capabilities but also enough muscle to exercise them. More computing power also usually means more battery power. For this camera, Olympus decided to bite the bullet and introduce a new, larger battery. They must have been quite desperate to do it just like that: going from MarkI to Mark II of the same model designation. They knew they were going to make some people (including myself) quite unhappy, having them to carry yet another battery around. Look, traveling with the Mark II as my primary body, the E-M5 (or original E-M1) as a backup, and the tiny E-PM1 for real emergencies, I have to carry at least three different spare batteries and, even worse, three different chargers! Three stupid chargers, all for the same lithium-ion chemistry, all for the same voltage. Pleez. I may have to buy one of those third-party universal chargers Olympus warns us against. The new battery's symbol is BLH-1. At 74 g and 47.7 cm3, it is 42% heavier and 83% larger (in volume) than the BLN-1 used in the base E-M1: 52 g and 26.0 cm3. The charge stored is 1720 mAh, as compared to 1220 mAh, an increase of 41%.
Interestingly, while charge per unit weight stayed identical, charge per unit volume dropped by 22%. This a significant difference — one may suspect we are dealing with two cylindrical cells in a brick-shaped enclosure. (Two batteries inside are needed anyway, because the voltage provided by Li-Ion chemistry is 3.6 V, and the whole battery unit has 7.2 V.) And guess what? Two cylinders within a fitting box leave I will not be surprised if one day Olympus finds a subcontractor capable of filling the whole brick volume, so that we will see a new, improved BLH-1, storing 2240 mAh or so. One last piece of trivia. The so-called CIPA battery rating for Mark II is 440 frames, for the original E-M1 — 350 frames. That's a nice improvement, but note that the charge spent per one CIPA frame increased (slightly) to 3.9 mAh up from 3.5 mAh. While the E-M1 cameras do not have built-in flashes, both come with tiny hot-shoe units, drawing the power from camera's battery. The flash units are mutually incompatible: Mark II does not have the accessory port, and Mark I is missing the fourth small pin in its hot shoe. Both these units can be used for remote control of other flashes from the Olympus system, but this is a separate story. Both units differ in a number of ways. First, the new one (FL-LM3) has more power, with a guide number of 9.1 (meters at ISO 100). The older FL-LM2 has a GN of 7.0 at the same ISO. In other terms, the new flash has a 30% longer reach (at the same ISO and F-number). This means that it is 70% more powerful (ratio of guide numbers, squared). We are lucky to have a bigger battery in Mark II. At the native ISO rating of 200, shooting at F/2.8 the new flash has a reach of 4.6 m. This will double at ISO 800, quadruple at ISO 3200. Second, the new unit has a wider coverage, corresponding to a focal length of 12 mm, as compared to 14 mm on the original. | ||
|
Last but (by far) not least: the FL-LM3 (left) has both tilt and swivel! Yes, you can shoot with it in bounced light — just use ISO 3200, where images are still very presentable and the GN rises to 36. And the darn cute thing makes you smile every time you look at it.
Olympus E-M1 Mark 2 with 12-40/2.8 PRO at 35 mm; |

| |
|
And one more minor change to how flash works: the maximum shutter speed for which you can use flash is now 1/250 s (1/320 s in Mark I). This signals some changes in shutter construction and/or operation, a slight slowdown of curtain travel. As the energy dissipated by vibrations is proportional to the travel speed squared, it was reduced in Mark II by almost 40% — a possible (but not the only possible) rationale behind the change. I checked that both cameras work fine with two legacy Olympus flashes: the mid-size FL-36 and the small, simple FL-20. The pre-flash TTL Auto mode is fully functional, and even the FP multi-burst mode (FL-36 only) for shutter speeds faster than 1/250 s works as it should. From other legacy models, I'm sure the FL-50 is fine, while the older FL-40 will behave just like non-dedicated, thyristor unit. The AF system in E-M1 was quite revolutionary, and not just for Olympus. Some photosites in the imaging sensor were re-assigned from the task of collecting image information to that of providing data for phase-detection AF, while the contrast-detection AF still uses, as usual, imaging photosites. Depending on application and circumstances, one or the other method (or both combined) may work best. I am not going here into the published details of the Olympus' hybrid AF solution; its description (two sections) in my E-M1 review is still valid. The system was, however, seriously rebuilt. On one hand, number of AF zones increased from 81 to 121; on the other, all of them now have phase-detection AF capability, while in the older model only a central cluster of 37 did. | ||
E-M1, μFT lens | 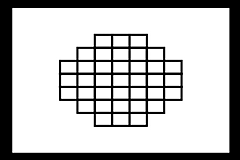
E-M1, FT lens | To see that change, mount a legacy FT lens on both cameras. On the older one, the rectangular AF grid will change to a diamond pattern; on Mark II it will remain unchanged. |
|
The part of frame covered by the array stays roughly the same. I noticed, however, two minor changes: (i) the small-target option is no longer available, and (ii) an option to use a cross-shaped group of 5 spots has been added. Frankly, I never had a need for either of these two features and never used them. In 90% of my shooting I just lock the focus set by a single, central spot (moving it around in tripod sessions only), so that I decide where the focus is set. This, of course, changes if you want to use face detection, or if you shoot sports, children, or other scenes with moving (and often unpredictable) subjects, what calls for use of continuous AF, often with tracking. While Single AF on OM-D cameras was excellent from day one, Continuous AF was raising some complaints (not that I've noticed, staying most of the time in my small, cozy S-AF world). Now Olympus says they have vastly improved the C-AF performance, and all reports I have read confirm this claim, some in the most enthusiastic manner. Being the kind of photographer I am, I haven't checked this myself; maybe in the coming weeks, as days become warmer and I spend more time outside... In Single AF, where I care most, the performance is very good, both speed- and accuracy-wise — but so it is on the original E-M1. I wasn't able to see any difference when using both cameras side-by-side. This is also the case with legacy, FT lenses, although here I was sort-of-hoping for some improvement. No change: they still work as they did on Four Thirds bodies — but no better, not at the level we've learned to expect, spoiled by μFT gear. As of this writing (February, 2017) Olympus is making two lenses with in-lens IS. This is supposed to work in addition to (not instead of) the in-body IS. The dual IS capability was added to the original E-M1 in a firmware update, so both cameras have it. The IS lenses are the MZD 300/4.0 ED IS PRO and MZD 12-100/4.0 ED IS PRO, but I'm sure others will follow (especially longer ones). Olympus also says that both dual- and single-mode IS in Mark II has been largely reworked (not just tweaked), so the IS brings up to 5 EV advantage in handholdable speeds with non-IS lenses, and up to 6.5 EV for IS ones. As I already wrote elsewhere, the only thing "up to" really means is "no more than". For this and a number of other reasons, I did my own IS tests with both cameras, using a number of lenses. While my results came nowhere near the claimed 5 or 6.5 EV, I still consider the numbers most impressive, especially on Mark II, showing solid (if not revolutionary) improvements over its predecessor. For the 12-100/4.0 IS lens at 100 mm, Mark II gains 4.3 EV in handholdable shutter speeds (this means exposures 20× longer). The older E-M1 shows, for the same lens, a gain of 3.6 EV (12×). For non-IS lenses the effect is less dramatic, but still clear, especially at greater focal lengths. For example, for the MZD 75-300/6.8-6.7 ED at 300 mm, Mark II gains 3.1 EV (8.4×), while the original E-M1 just 1.9 EV (3.6×). | ||||||||||||||

IS Off | 
IS On | |||||||||||||
|
1:1 scale samples: E-M1 Mk.II with 12-100/4.00 IS PRO, 1.4 s handheld Each sample typical for a series of 20. Click to view full images. Images equalized, otherwise unaltered. Please note that characters on screen are anti-aliased! | ||||||||||||||
|
Image processing consists, roughly speaking, of two stages. The first one is scanning the imager's rows of photosites, reading the accumulated charges, converting those to numeric values and building out of those a raw image file. That is not really an image file, as it does not contain direct information on colors of individual pixels. This raw image information has to be converted to the actual RGB image or saved to memory card for such conversion later (or both). The raw-to-RGB conversion is the second stage of image processing; some important adjustments (white balance, sharpening, denoising, tonal adjustment, and more) happen at this stage. Some adjustments or corrections can be performed on either of these stages. Looks like there is a recent trend of more and more of them creeping from stage two into stage one, with raw image files becoming rather not-so-raw, and with manufacturers not eager to share this information with camera users. Thus, if conversion in postprocessing allows you to change some image properties, others are already hardwired into the not-so-raw file. I'm not concerned about where this line is drawn (or redrawn), as I'm saving all my images as camera-generated JPEGs. Therefore in this section I will not go into what changes were introduced at which stage — I will treat the whole exposure-to-JPEG process as one. I will not go into a "why not raw" discussion, sorry. Still, feel free to read my Raw Image Format article and/or an excellent piece by Ken Rockwell on this subject. First of all, Olympus claims further improvements in imaging at the highest ISOs. While color and tonality were already holding very nicely in Mark I all the way up to ISO 25600, there was visible noise above ISO 6400. Now, I am not allergic to noise in my images as long as it is nice and even — without clustering in larger blobs, that is. This was showing up in Mark I at ISO 25600 and, to a lesser extent, 12800. My image samples show that the problem is gone (or almost so) in Mark II. At ISO 25600 it assures images like Mark I did at ISO 12800, perhaps even 6400. It looks, however, that this improvement comes at a price of a visible drop in detail and contour sharpness. While I already posted and discussed a comparison of image samples, I will be rerunning it in a more structured fashion, to confirm or dismiss the sharpness loss. Then I will modify this section as needed. An interesting and, I think, useful new adjustable parameter (or three) in image processing: separate adjustments to shadows, highlights and midtones. Especially the midtones, which are the most commonly tweaked thing in my (minimal) postprocessing of in-camera JPEGs. I gave this new feature a try or two, but to see how really useful it may be, I have to get more familiar with it. I have, however, two complaints here:
E-M1 Mk.II is a real speed demon in serial shooting, even compared to Mk.I which was already very speedy: | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
|
As I haven't done any experimenting with serial shooting on Mark II yet, I can only quote the data as provided by Olympus. The "electronic shutter" is not really a shutter: the image sensor remains exposed to light all the time, while the collected charge is being read from photosites row by row when the picture is being taken. Each row is being updated up to the very moment when its readout begins, so different rows show the scene at slightly different instants of time. This readout mechanism is, in a sense, similar to a vertical-travel, focal-plane shutter in cameras going back as much as 100 years. Like that shutter, for moving objects it may cause a number of geometric distortions in the image, depending on the combination of movement directions. See here for more about this effect, and perhaps the most famous example, shot in 1912. The magnitude of this "roll effect" is directly proportional to the time elapsed between reading out the first and the last line of photosites (regardless of exposure time). This time is not quite negligible: in Mark I it was 1/15 s, typical for the industry. According to Olympus, this readout time has been reduced to 1/60 s in Mark II, so the distortions are also 4 times smaller. A great improvement if you use electronic shutter for fast-moving objects (or if you pan your camera a lot). I don't. The mechanical focal-plane shutter, like the one used in OM-D cameras or SLRs, can also create this effect, with its magnitude defined by the shutter travel time. For the E-M1 Mk.II the travel time is 1/250 s, so the roll effect is 4 times smaller than the one created by the improved electronic shutter. This is a smart and entertaining variation on the drive mode theme, made possible by some of other improvements (higher shooting rates, faster AF, larger image buffer, possibly more). It allows you to capture moments otherwise impossible to catch. There are actually two Pro Capture modes, both using electronic shutter, but differing in maximum frame rate (18 and 60 FPS). Yes, the high-rate mode freezes AE and AF at the first frame, which limits its usability to stationary objects. Half-press and hold the shutter release while following the action in the viewfinder. The camera will start recording a series of frames with the rate as set. They are not written to the card, though, being only stored in the image buffer. When the buffer holds 14 frames (or fewer, as previously defined), the oldest frame is deleted from it to make room for the next one; at any moment the buffer holds the last 14 frames recorded. Then something worth recording happens. You could not know it ahead of time, but if you fully press the release soon enough, you will have that moment in one of buffered frames. At 18 FPS you have 3/4 of a second to react, plenty of time. The camera now starts writing the buffer out to memory card, while still taking pictures, as long as you keep the release fully pressed. The process ends when you let go of the button, or reach the pre-set sequence limit. You end up with a sequence of a few dozen images, from which to choose the keepers. This is much more efficient than shooting a series just because you anticipate something may happen. Some cameras allow you to convert a selected frame of a movie into a still picture. This is not quite the same: the movie has to be recorded to memory card, and its resolution is much lower than that of a still picture. This feature, first introduced in the E-M5 Mk.2, allows for images with resolution higher than the nominal one, defined by pixel count; obviously, with some additional conditions:
The camera exposes eight frames in a high-speed sequence: two groups of four frames each. The sensor is shifted after every frame, so that each group is a square with a side of one pixel. The shift between groups is half of that pitch vertically and horizontally, i.e., a total of .7 pitch diagonally. A standard 20-megapixel Bayer matrix image uses approximately 5 MP worth of information from a single exposure (see Is Megapixel a Megapixel?), and no amount of postprocessing can change that. The E-M1.II Hi-Res mode uses two arrays. Each is 20 MP big, and based on four exposures (full 20 MP of information, not just 5). This improves not only sharpness (with a lens good enough), but also noise and dynamic range, at the same time reducing some common demosaicing artifacts. To accommodate the extra detail, RGB images and/or raw files of 25, 50 or 80 megapixels in size are generated. This is described in a related article: E-M1 Mk.II High Resolution Mode New in Mark II are two SD Card slots, instead of one. They can be configured in a number of sometimes confusing ways, in series (second one used after the first is full) or parallel (each picture written to both), with the second option having multiple flavors: what happens when one card is full, different image sizes or file types for each card, you name it. Things are further complicated by the fact that, while both slots support SDHC and SDXC cards, only one has pins fully compatible with the UHS-II bus (speeds of 156-312 MB/s); the other supports only UHS-I (50-104 MB/s). A card mismatched with the slot will still work, but only with the UHS-I speed. Yes, so we really have four card type/speed combinations, usually shown at the label as SDHC I, SDHC II, SDXC I and SDXC II. For our purposes, only the distinction between I and II is important. I found this information in this Wikipedia article. While using a UHS-II card in Slot 1 gives you higher writing speeds, if you don't do UHD or high-FPS movies, this will be only for bragging rights. What I bought for Mark II was a pair of Lexar Professional 633x 128GB SDXC UHS-I cards on Amazon, for the total of $65, setting them up to work in series. Next time I travel, I set them up in a parallel (backup) configuration, to keep the images safer. Oops! The monitor display for the number of remaining frames has a problem: it uses only four digits. If the number is too large, 9999 is shown. Like its predecessor, Mark II uses multiple user interfaces (often three, sometimes four, even five) to perform the same task or adjustment. Never having been good at skinning cats, I rather disliked this practice and I still do. Mercifully, you can hide at least some of these interfaces, and also disable the touch screen (which I did five minutes after unpacking the camera). Now, a bit better. Here, however, we are supposed to focus on differences between Mark I and Mark II, so back to the subject. The best piece of user interface Olympus ever came up with was the Control Panel. This was later renamed to SCP, or Super Control Panel, as the brightest minds of Shinjuku are working on changing that to Super Pro Control Panel Pro. Introduced, if I remember right, in the E-300 SLR back in 2004, its concept is simple but powerful: the basic picture-taking and image-conversion parameters visible at a glance, with cursor keys used to select ones to modify. Unfortunately, higher monitor resolution on the E-M1 resulted in the simplicity spoiled with the proverbial kitchen sink: about 13% of the grid area is taken by a field showing just one (at a time, that is) of camera's current button assignments and providing a shortcut to the button-defining branch of the Settings menu. This is a double violation of the original SCP principles: (i) the display is no longer at-a-glance, and (ii) no longer limited to image-affecting parameters. For crying out loud: this has nothing to do with the resulting image! The button assignment function has been chosen arbitrarily, like in a desperate attempt to fill the suddenly available extra space. Besides, once you set the buttons to your liking, how often do you change that? Once a year? For me, this is the ugliest aspect of the E-M1 user interface, as it breaks one thing Olympus really got right in it. In Mark II the problem has been partially fixed. The large field (taking almost half of a double row of items) is gone, replaced with one 1/4 of the previous size, providing just a shortcut to the button-setting menu branch. The double violation still remains, but it is less obtrusive. I only hope the shortcut will go away one day. Sorry, I'm not done with the Control Panel yet. It s just too important to just glance over. The designers still had the extra space to fill. This time (Mark II) they decided to add a bunch of movie-related parameters. This also seems, to me at least, a sub-par decision. The display loses its original advantage, simplicity. It would be better to have two Control Panels: one for movies and one for still photography, with the [Info] button used to switch between them (like it was for the Flash Control Panel in some E-Series SLRs). Additionally, a panel you don't want to use could be removed from the [Info] sequence exactly like some control interfaces can be removed from it now. Bang, you have both power and simplicity, everyone is happy. Last but not least, the space freed this way could be used for display of (and access to) something genuinely useful, like Noise Filtering. This setting deserves a place among Picture Mode parameters and I am really surprised it is still not there. Bracketing is another candidate, but not before the whole bracketing mess in OM-D cameras is cleaned up. Don't even get me started on this. Or on the mess with drive modes. Both can be improved, gaining more logical structure, while not giving up the power. Now, the menu system. With the number of camera customization and configuration options traditionally available on Olympus cameras, it will never become really simple and easy to use. You just have those 300 parameters to set or options to choose from. Still, there is always room for improvement. Lots of it. The menus in Mark II have been visibly improved from Mark I. This said, they are still quite bad. The remaining problems can be roughly divided into three groups:
An example of the problem of the second kind; thankfully, fixed in Mark II (but why not in Mark I, with all those firmware updates?). In the branch dealing with user-defined presets, there are some menu items named [Set]. It is unclear if they refer to
Well, it turns out that it means one thing on one menu level, the other on the next. Yeah, I could just memorize it, or to figure it out each time, but what is wrong with using two plain English words here: Store and Recall? This is how it is in Mark II. Examples of open issues. Why do I turn WiFi in the Setup menu, but connect with a cell phone (or a tablet) from Playback? (This was the last place I looked into.) Why are most of display-related settings in Custom Menu D, except for the color/contrast and post-view duration which are in Setup again? Excuse me, this is not just a matter of taste; this is a matter of logic. My guess is that fifty, maybe a hundred small but useful changes to the menu system have been introduced in Mark II, and a similar number is still needed to make it more civilized. Let us just wait and hope. Like most digital cameras nowadays, the E-M1 has a capability of shooting movies. While this used to be my major passion decades ago (the era of 8 and 16 mm film), one day I gave it up, never to return. In order to do it right, I would have to organize my whole life around this activity, and I was not willing to do that. Besides, even if I was a president of the largest movie-making club in my town (also hometown of Roman Polanski at that time), my movies stank to heaven. Really. Anyway, with this not being my area of expertise or interest, I don't feel qualified (or motivated) to write on the subject. Sorry, you have to look elsewhere. Just a reflection: Mark II, as I have heard, adds the capability to record video in UHD (3840×2160 pixels), at 30 FPS. This seems most impressive technically: 8-megapixel frames, 30 times per second? The original E-M1 was, warts and all, the best camera I've used so far until the arrival of Mark II. This one, while not introducing any ground-breaking changes, improves upon its predecessor in dozens of often (but not always) small changes, and they all add up to a noticeably better user experience and, as importantly, produced results. While Mark II still leaves room for improvement (some of which I hope to see in upcoming firmware revisions), for me it becomes the new king of the hill. Long live the king. The not-so-good news is the pricing. Two grand is no small change; that's $500 more than Mark I was at the release. Well, for a premium product you may expect to pay a premium price. The camera was long out of stock at B&H, reappearing just a few days ago — somebody is buying it. If you are reading this article, this probably means that you already have the original Mark I, or seriously consider(ed) getting it. Now you have to make your mind whether to get the Mark II instead of, or in addition to, that choice. Here is my advice. If you already have the older model, don't rush into buying the new one — unless your photography strongly depends on one or more of new (or upgraded) features: insanely fast serial rate, Pro Capture, or (just maybe) improved image stabilization. For 95%, perhaps more, photographers, this is not the case; they will be better off enjoying another three good years with the camera they already have. No, you don't really need those four more megapixels. If you are itching to spend that money, treat yourself to a really good lens (like the 12-100/4.0 IS or 12-40/2.8) or to a lighter, smaller and most enjoyable backup body (like the Pen F). If you are considering the original E-M1 at a current, heavily discounted, price, it depends. If you can find a new body with warranty below $600 (US), go for it; it's a steal. Above $900 or so I would rather bite the bullet and spend $2000 on Mark II. Anything in-between is a gray area, with the right (?) decision depending on a number of individual factors. If you have invested into some premium Four Thirds optics and want to use it on more current cameras, you will need an E-M1 — preferably Mark II, but a Mark I will do if you are on a budget. Only these two models use the sensor with phase-detection AF support, necessay for FT lenses.
If this is your first OM-D camera, consider the less-costly, but very attractive, alternative: the E-M5 Mk.II. You give up the a few secondary features, saving more than 50% of your money (spend it on lenses). Or, again, go for the | ||||||||||||||
|
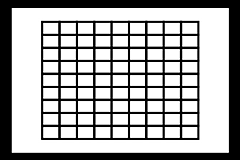
The last group includes also newcomers, curious about jumping on the μFT bandwagon. If you are one, you might have read how inferior this imager size is compared to vastly larger APS-C format, used by Canon, Nikon, and many other makers in their less-than-full-frame SLRs (and in some non-SLR ILCs). You cannot argue with a mule, so here is just a picture comparing both frames. Draw your own conclusions. |

Outer white box; APS-C (Canon) |

|
My other articles related to the |
| This page is not sponsored or endorsed by Olympus (or anyone else) and presents solely the views of the author. |
| Home: wrotniak.net | Search this site | Change font size |
| Posted 2017/03/07; last updated 2017/05/24 | Copyright © 2017 by J. Andrzej Wrotniak |